Dataset Preparation
In this study, dataset training/validation/test are prepare as numpy .npy array image. Since this is geospatial deep learning, We need to sample the data from raster image.
Raster preparation
First, prepare input raster image, number of the layer depends on your study , for example we have sentinel 2 and sentinel 1 stack togeter. Band order is not important since deep learning will extract feature by itselt.
Example of band order
[B2,B3,B4,B5,B6,B7,B8,B8A,B11,B12,VV,VH]
Explore Sentienl1-2 , GEDI to learn more about raster preparation.
Raster comes in tiles system. To sample the data in the same area, some position can be overlap between tile. Recommended method is mosiac raster into one then process to sampling the data.
But geospatial data can use heavy computational resource, require a lot of memory. A workaround is to use python library like rasterio and implement window reading and write temporal data to disk using tempfile.
A code snippet for mosiac raster.
from tempfile import mkdtemp
import rasterio
from rasterio import Affine
from rasterio import windows
import math
import numpy as np
import os
# Set the output mosaic file path
OUTPUT_PATH = ... # replace wil desire path
OUTPUT_NAME = ... # replace wil desire name
input_path = ... # path include all of raster need to be mosaic
INPUT_FILES = [os.path.join(input_path,file) for file in os.listdir(input_path)]
sources = [rasterio.open(raster) for raster in INPUT_FILES]
memmap_file = os.path.join(mkdtemp(), 'test.mymemmap')
# adapted from https://github.com/mapbox/rasterio/blob/master/rasterio/merge.py
first = sources[0]
first_res = first.res
dtype = first.dtypes[0]
# Determine output band count
output_count = first.count
# Extent of all inputs
# scan input files
xs = []
ys = []
for src in sources:
left, bottom, right, top = src.bounds
xs.extend([left, right])
ys.extend([bottom, top])
dst_w, dst_s, dst_e, dst_n = min(xs), min(ys), max(xs), max(ys)
out_transform = Affine.translation(dst_w, dst_n)
# Resolution/pixel size
res = first_res
out_transform *= Affine.scale(res[0], -res[1])
# Compute output array shape. We guarantee it will cover the output
# bounds completely
output_width = int(math.ceil((dst_e - dst_w) / res[0]))
output_height = int(math.ceil((dst_n - dst_s) / res[1]))
# Adjust bounds to fit
dst_e, dst_s = out_transform * (output_width, output_height)
# create destination array
# destination array shape
shape = (output_height, output_width)
# dest = np.zeros((output_count, output_height, output_width), dtype=dtype)
# Using numpy.memmap to create arrays directly mapped into a file
dest_array = np.memmap(memmap_file, dtype=dtype,
mode='w+', shape=shape)
dest_profile = {
"driver": 'GTiff',
"height": dest_array.shape[0],
"width": dest_array.shape[1],
"count": output_count,
"dtype": dest_array.dtype,
"crs": '+proj=latlong',
"transform": out_transform
}
# open output file in write/read mode and fill with destination mosaick array
with rasterio.open(
os.path.join(OUTPUT_PATH, OUTPUT_NAME),
'w+',
**dest_profile
) as mosaic_raster:
for src in sources:
for ji, src_window in src.block_windows(1):
print(ji)
r = src.read(1, window=src_window)
# store raster nodata value
nodata = src.nodatavals[0]
# replace zeros with nan
r[r == nodata] = np.nan
# convert relative input window location to relative output window location
# using real world coordinates (bounds)
src_bounds = windows.bounds(
src_window, transform=src.profile["transform"])
dst_window = windows.from_bounds(
*src_bounds, transform=mosaic_raster.profile["transform"])
# round the values of dest_window as they can be float
dst_window = windows.Window(round(dst_window.col_off), round(
dst_window.row_off), round(dst_window.width), round(dst_window.height))
# before writing the window, replace source nodata with dest nodata as it can already have been written (e.g. another adjacent country)
dest_pre = mosaic_raster.read(1, window=dst_window)
mask = (np.isnan(r))
r_mod = np.copy(r)
r_mod[mask] = dest_pre[mask]
mosaic_raster.write(r_mod, 1, window=dst_window)
os.remove(memmap_file)Sampling data
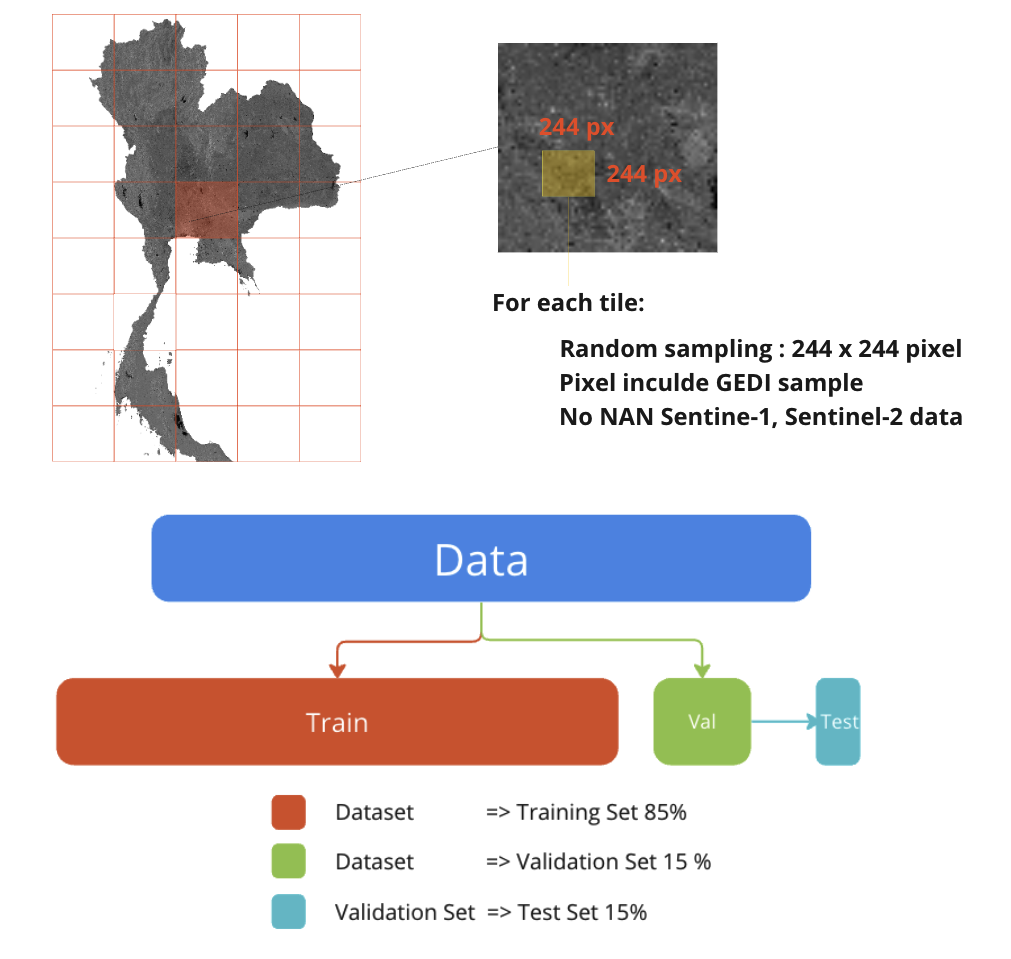
After you have complete mosaic raster for you target area (both input and ground truth). We need to sampling the data into desire size so we can feed into model. For example U-NET commonly use 244x244px image but since it is convoluional neural network, it suppot any size. Only constrain is time and computational resource.
Keep that in mind that we are dealing with geospatial data. All three split (train/test/val) must not be duplicates, and overlapping. Clearly speaking there must be no spatial overlap. the reason is to avoid model bias and dataset shift.
Start by defining the sampling area (Window sampling) by selecting an area of 244 x 244 pixels, which is a common image size used in Deep Learning because it is large enough to be able to capture important details in the picture while still not cost to much computational resource. Then randomly select areas in Thailand using discrete uniform sampling and check the validity of the satellite image data, both Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 must not be null data (NaN) and must have GEDI data footprint in the image.
split the sampling into 3 sets of data: 85% training set data, 15% validation data set for evaluating the accuracy of the model during learning, and 15% test set data for evaluating the model accuracy. after learning is complete, divided from 15% of the validation set.
However, the random selection of the three data sets did not have any form of random selection position. But the distribution must be taken into account. Randomly selected with equal probability.
Example code for random sampling the data :
Warning
This code have O(n^2) time complexity, use for guideline only since it still does not optimize.
for sample in tqdm(range(NUM_SAMPLE)):
# random row start and col start
row_start = np.random.randint(0, IMG_HEIGHT-244)
col_start = np.random.randint(0, IMG_HEIGHT-244)
# patch rasterize GEDI
gedi_subset = extract_raster_array(row_start, col_start , GEDI_TARGET_PATH)
# patch input
sentinel_subset = extract_raster_array(row_start, col_start , COMP_INPUT_PATH)
# pathch ESA
esa_subset = extract_raster_array(row_start, col_start , ESA_PATH)
# if all GEDI pixel = 255 (all NAN) or sentine 2 has any pixel = 0(NAN) : random row start and col start again
while((np.all(np.isnan(gedi_subset))) or (np.any(np.isnan(sentinel_subset)))):
# random row start and col start
row_start = np.random.randint(0, IMG_HEIGHT-244)
col_start = np.random.randint(0, IMG_HEIGHT-244)
# patch rasterize GEDI
gedi_subset = extract_raster_array(row_start, col_start , GEDI_TARGET_PATH)
# patch input
sentinel_subset = extract_raster_array(row_start, col_start , COMP_INPUT_PATH)
# pathch ESA
esa_subset = extract_raster_array(row_start, col_start , ESA_PATH)
#if count > (valiaton set)
if (sample > int(0.85* NUM_SAMPLE) - 1):
#get index of pixel where value of ESA classification == 50 (urban area)
urban_flag_idx = np.where(esa_subset == 50)
band = urban_flag_idx[0]
row = urban_flag_idx[1]
col = urban_flag_idx[2]
# change value of GEDI rasterize in urban area to (NAN)
gedi_subset[band,row,col] = np.nan
#random name
random_name = strgen.StringGenerator("[\w\d]{10}").render()
filename = random_name + '.npy'
# Check name in folder (os.listdir)
# File List
name_list_train = os.listdir(target_input_train)
name_list_val = os.listdir(target_input_val)
#if name is redundant random name again
while((filename in name_list_train) or (filename in name_list_val)):
random_name = strgen.StringGenerator("[\w\d]{10}").render()
filename = random_name + '.npy'
# change all data to float 32
sentinel_subset = sentinel_subset.astype('float32')
gedi_subset = gedi_subset.astype('float32')
esa_subset = esa_subset.astype('float32')
# save all data
np.save(os.path.join(target_input_val,filename), sentinel_subset)
np.save(os.path.join(targetdata_gedi_val,filename), gedi_subset)
np.save(os.path.join(target_esa_val,filename), esa_subset)
else: #training
#random name
random_name = strgen.StringGenerator("[\w\d]{10}").render()
filename = random_name + '.npy'
# Check name in folder (os.listdir)
# File List
name_list_train = os.listdir(target_input_train)
name_list_val = os.listdir(target_input_val)
#if name is redundant random name again
while((filename in name_list_train) or (filename in name_list_val)):
random_name = strgen.StringGenerator("[\w\d]{10}").render()
filename = random_name + '.npy'
# change all data to float 32
sentinel_subset = sentinel_subset.astype('float32')
gedi_subset = gedi_subset.astype('float32')
esa_subset = esa_subset.astype('float32')
# save all data
np.save(os.path.join(target_input_train,filename), sentinel_subset)
np.save(os.path.join(targetdata_gedi_train,filename), gedi_subset)
np.save(os.path.join(target_esa_train,filename), esa_subset)